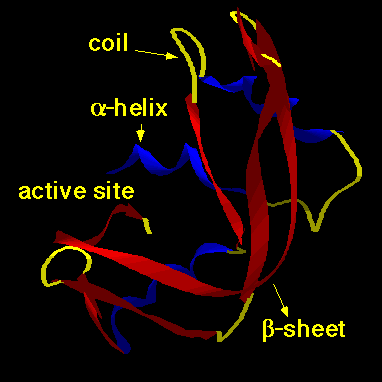
Protein catalysts are called enzymes.Proteins have structural features that give clues about their action. |
 |
Enzymes Day 2 (requested content/links)
You are here:
Protein catalysts are called enzymes.Proteins have structural features that give clues about their action. |
 |
Good graph of different catalytic reactions (substrates, products/intermediates) http://www.wheatgrass.com/book/chapter6.html
Change enzyme, substrate and equilibrium constants to see substrate go away and product appear in a time course experiment.http://www.rpi.edu/dept/chem-eng/Biotech-Environ/Canada/enzkin.html
human amylase, yeast catalase, potato catalase
|
Glucose and maltose do not stain with iodine while starch stains with iodine. Germinating seeds secrete amylase.
starch/iodine plate assay |
http://www.chemieunterricht.de/dc2/kristalle/protein.htm
http://www.cmbi.kun.nl/gv/ nielsen/amylase/
|
|
staph bacteria have catalase catalase is detected by bubbling after addition of hydrogen peroxide http://www.cat.cc.md.us/courses/bio141/labmanua/lab8/catstaph.html
|
http://www.chemieunterricht.de/dc2/kristalle/protein.htm
http://www.ineti.pt/proj/cienciaviva/unfab/proteinas.html
|
|
pepsin http://www.ineti.pt/proj/cienciaviva/unfab/proteinas.html human pepsin 1psn
http://dwb.unl.edu/Teacher/NSF/C10/C10Links/ main.chem.ohiou.edu/~wathen/chem302/protein.html |
|
potato and peroxidase